The Evolution and Technology Behind Automatic Glass Sliding Doors: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
This article delves into the history, technology, benefits, and future trends of automatic glass sliding doors, providing a comprehensive understanding of their role in modern infrastructure.

History of Automatic Doors
Early Innovations
-
Ancient Automatons (1st Century AD): The Greek mathematician Heron of Alexandria designed one of the earliest known automatic door mechanisms, powered by steam and water pressure. While not practical for everyday use, it demonstrated the potential for automated entry systems. -
20th-Century Developments: The first commercially viable automatic doors were introduced in the 1950s and 1960s, primarily in the United States. Companies like Stanley Works and Dewey developed basic motion-sensing doors, initially used in supermarkets to improve customer flow.
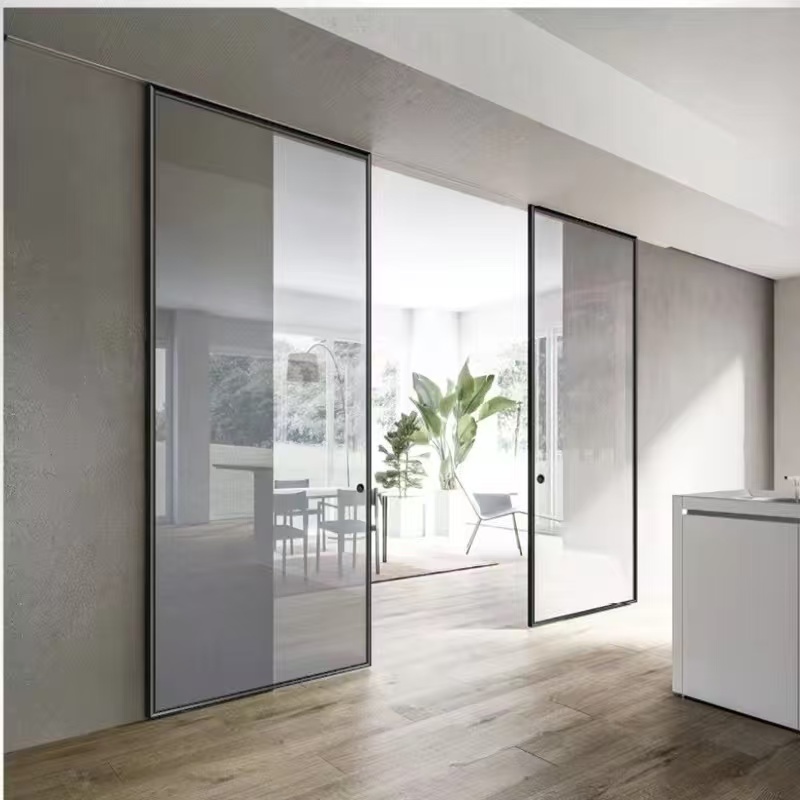
Rise of Glass Sliding Doors
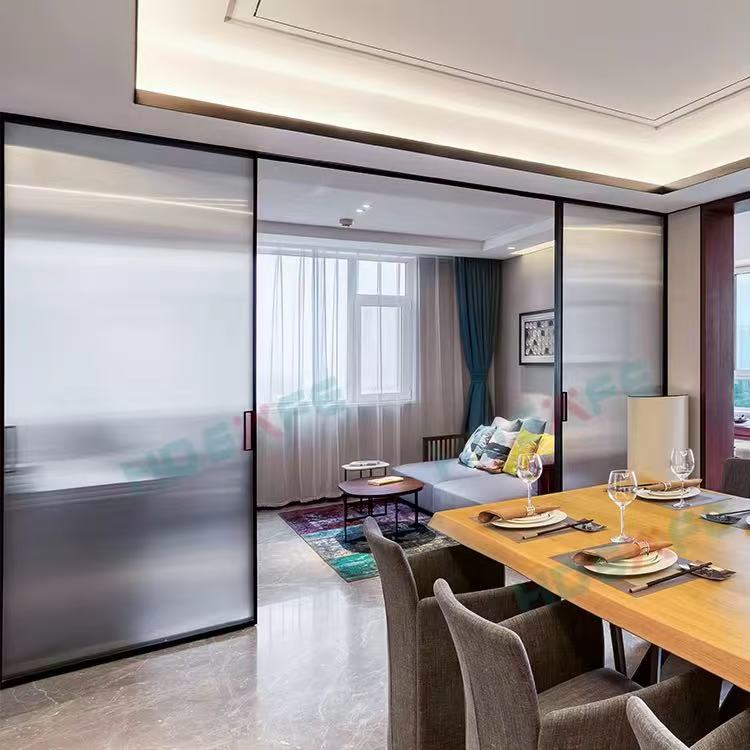
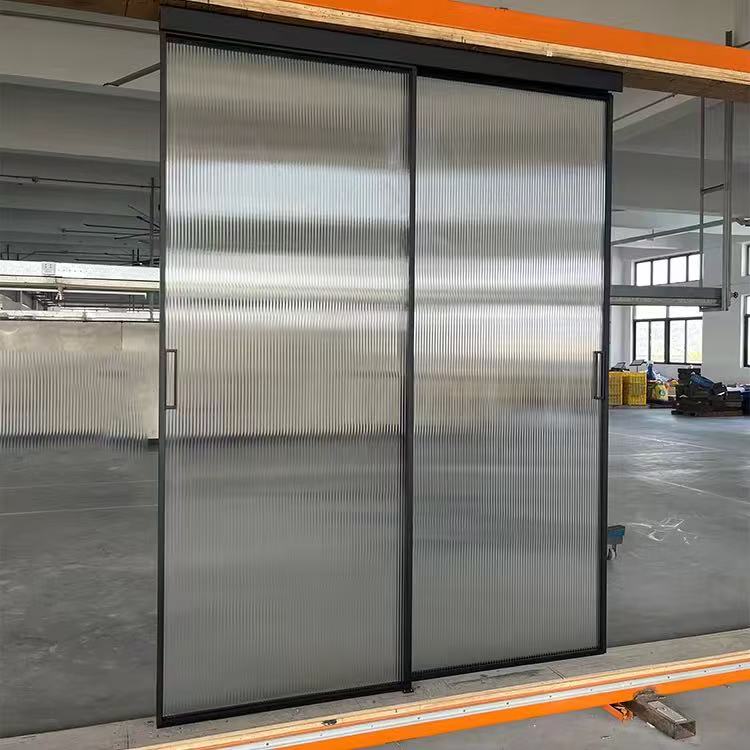
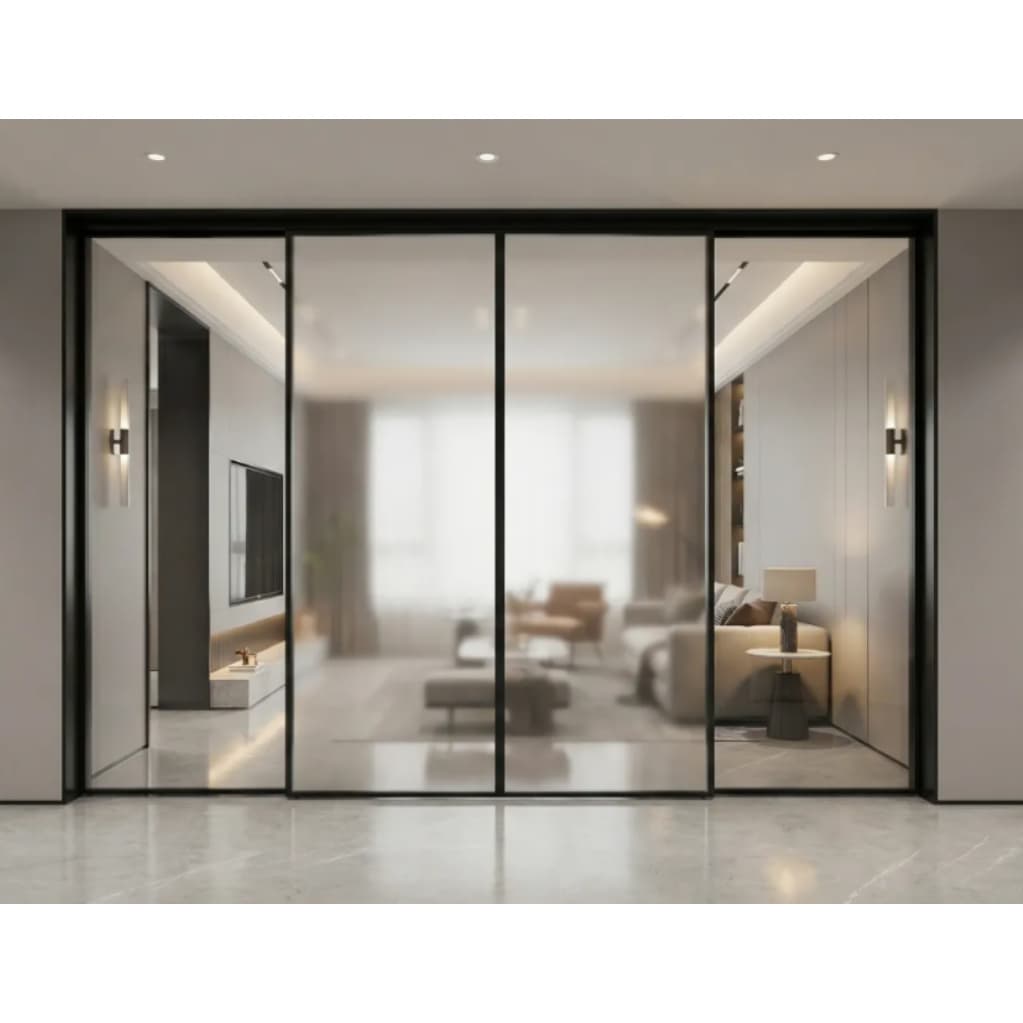
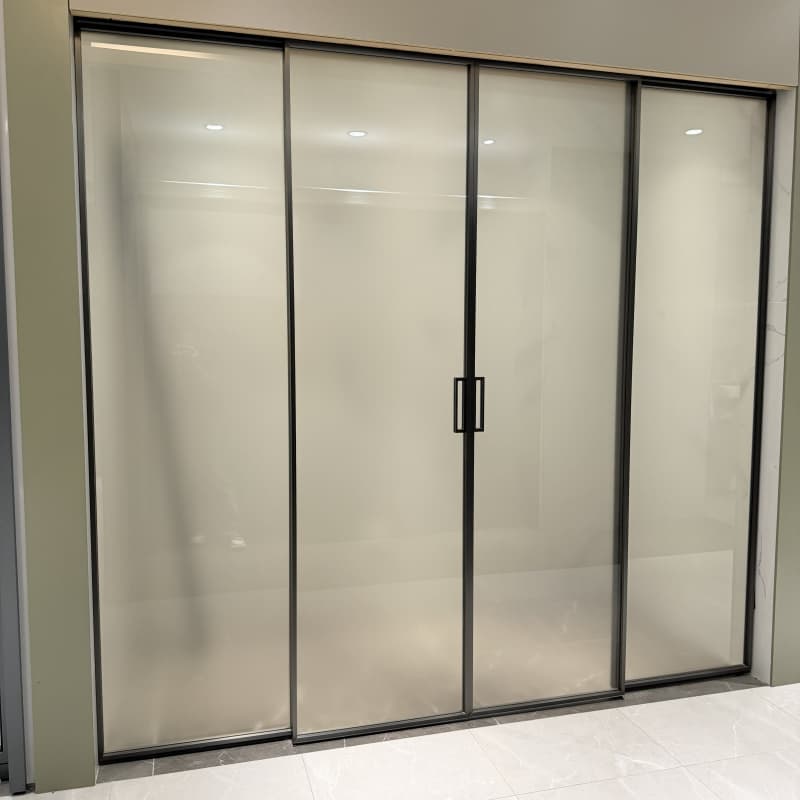
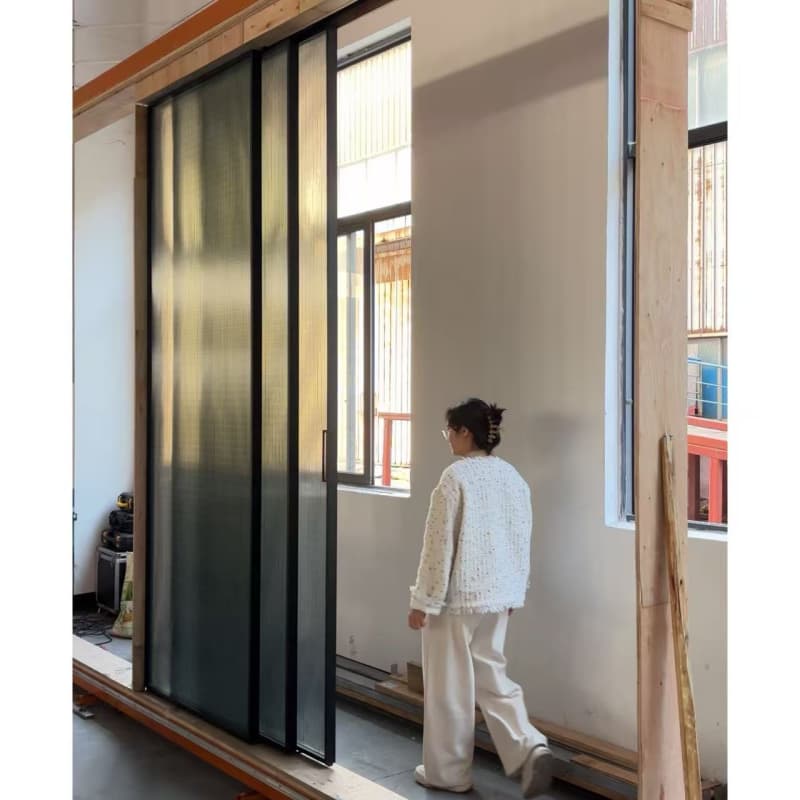
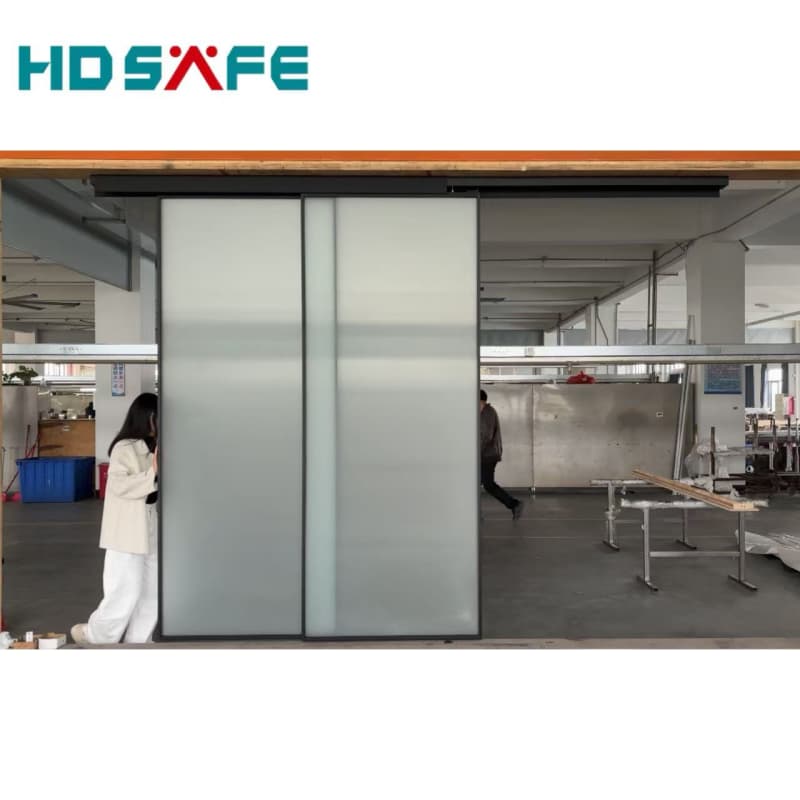
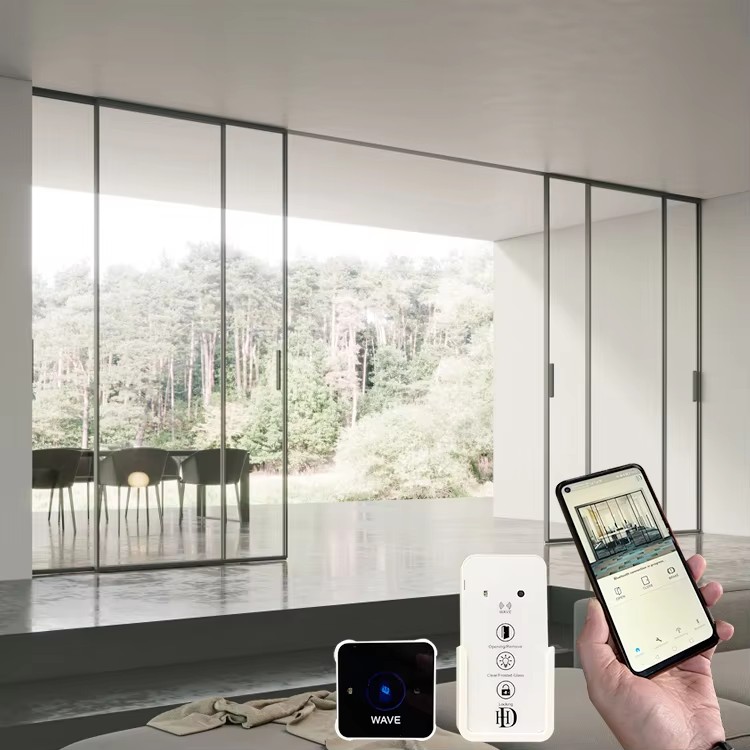
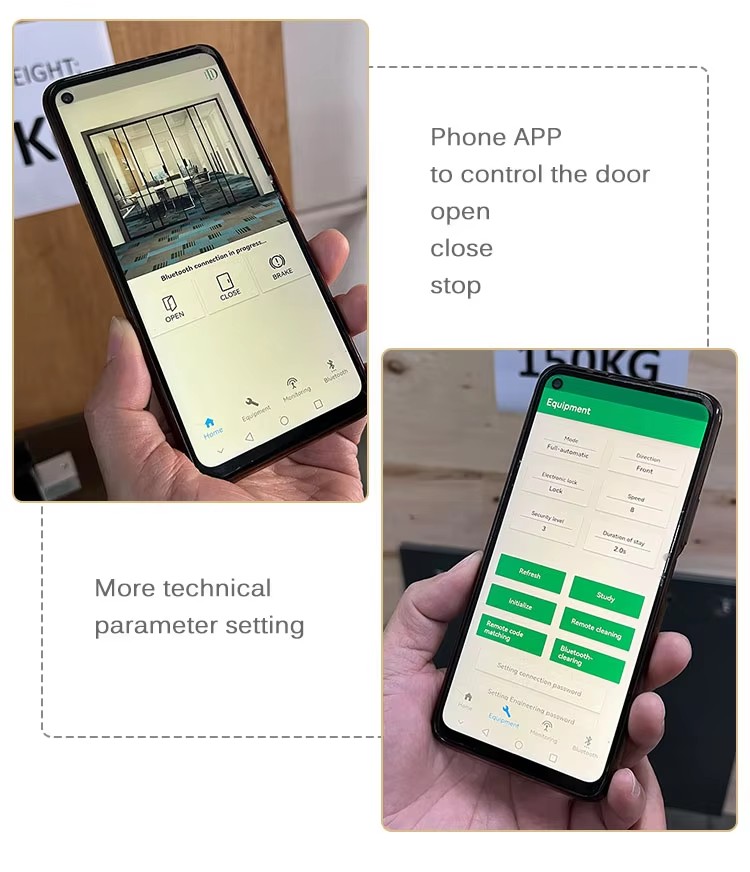
How Automatic Glass Sliding Doors Work
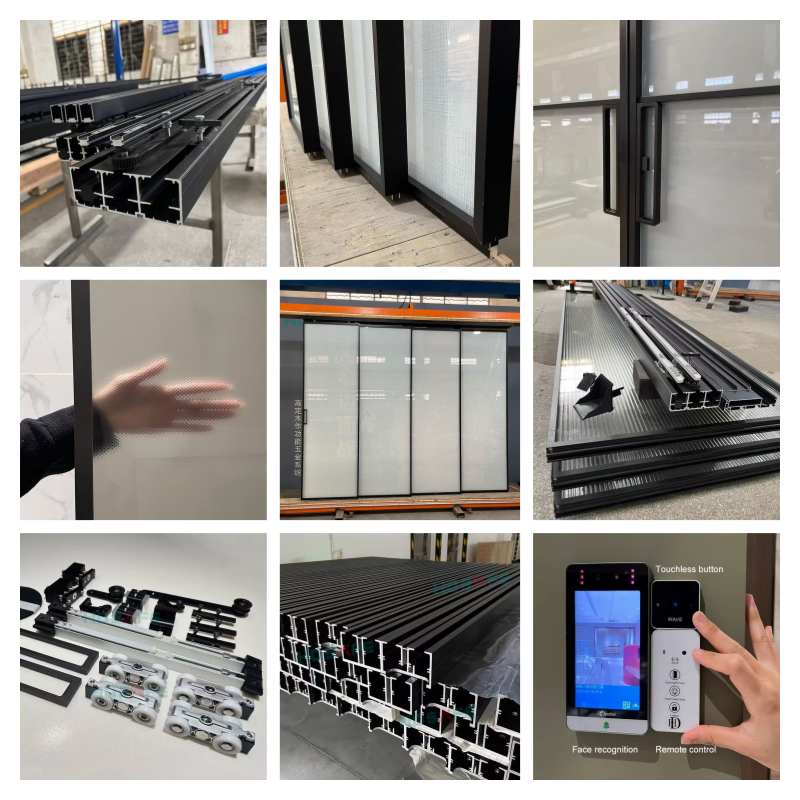
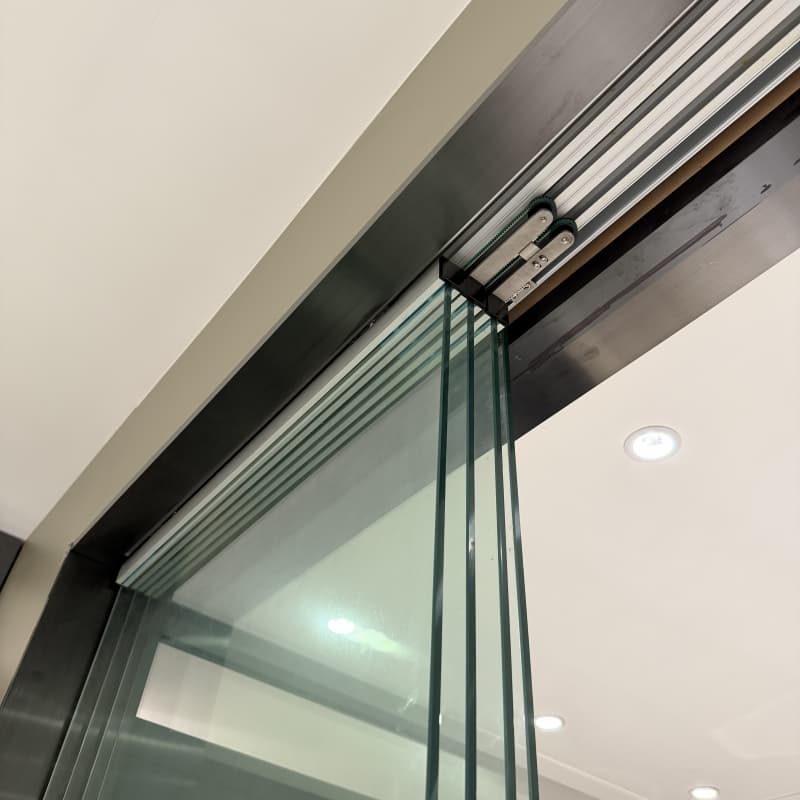
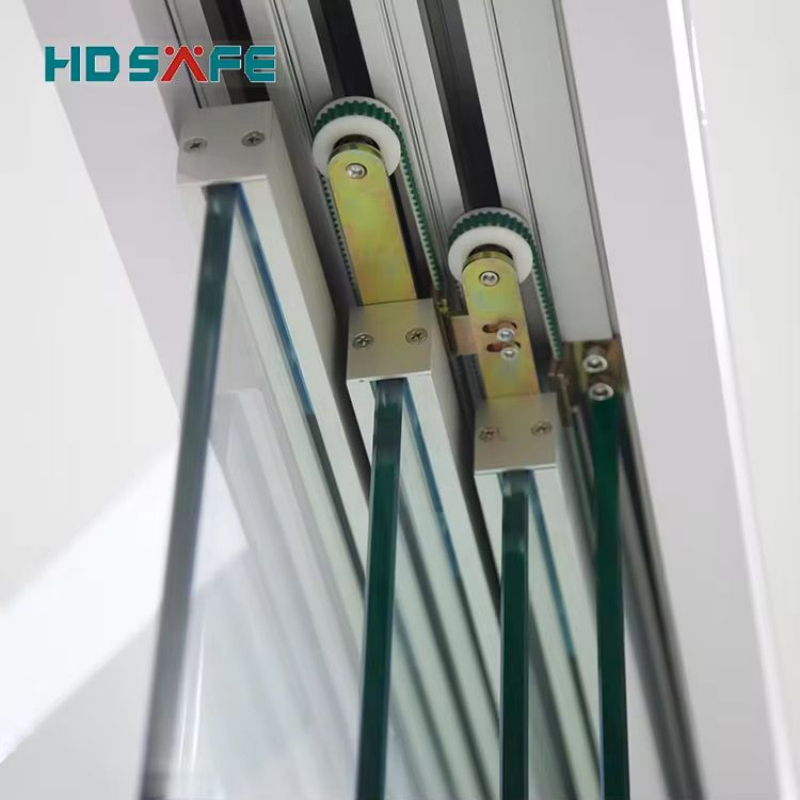
Key Components
-
Glass Panels: Tempered or laminated glass ensures safety and durability. The transparency of glass enhances visibility and architectural appeal. -
Sliding Track System: A concealed or exposed rail guides the door panels, allowing smooth movement. -
Motor & Drive Mechanism: Electric motors (often brushless DC or induction motors) power the door’s movement. Some systems use belt drives, while others employ direct-drive mechanisms. -
Sensors: -
Motion Sensors (Infrared/RFID): Detect approaching individuals and trigger the door to open. -
Pressure Sensors: Prevent the door from closing if an obstacle is detected. -
Proximity Sensors (Radar/Ultrasonic): Enhance accuracy in detecting movement.
-
-
Control Unit: Manages the timing, speed, and synchronization of door movements.
Operation Modes
-
Automatic Mode: The door opens when a sensor detects movement and closes after a set delay. -
Manual Override: Allows users to push the door manually if the system fails. -
Hold-Open Function: Keeps the door open for extended periods (e.g., during high traffic).
Benefits of Automatic Glass Sliding Doors
1. Enhanced Accessibility
-
ADA Compliance: Automatic doors are essential for wheelchair users, parents with strollers, and individuals with mobility challenges. -
Hands-Free Operation: Ideal for carrying groceries, luggage, or medical equipment.
2. Improved Energy Efficiency
-
Insulated Glass: Modern automatic doors often feature double or triple glazing with low-emissivity (Low-E) coatings to reduce heat transfer. -
Airflow Control: Minimizes drafts by opening only when needed, reducing HVAC costs.
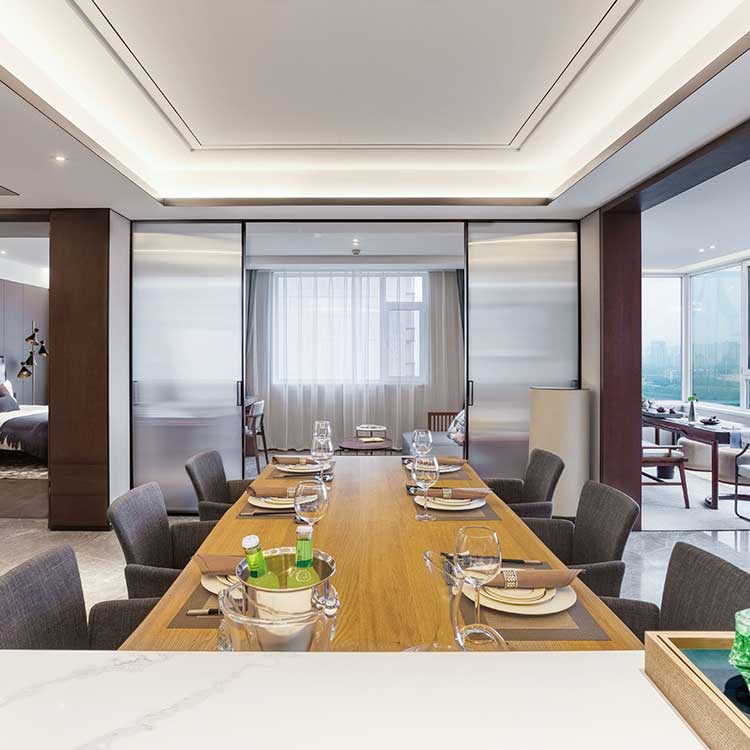
3. Aesthetic Appeal
-
Modern Design: Glass sliding doors create an open, airy feel, making spaces appear larger. -
Customization Options: Tinted, frosted, or decorative glass can match architectural themes.
4. Safety & Hygiene
-
Contactless Entry: Reduces germ transmission compared to traditional handle-based doors. -
Emergency Features: Some systems include breakaway panels for fire exits.
Types of Automatic Glass Sliding Doors
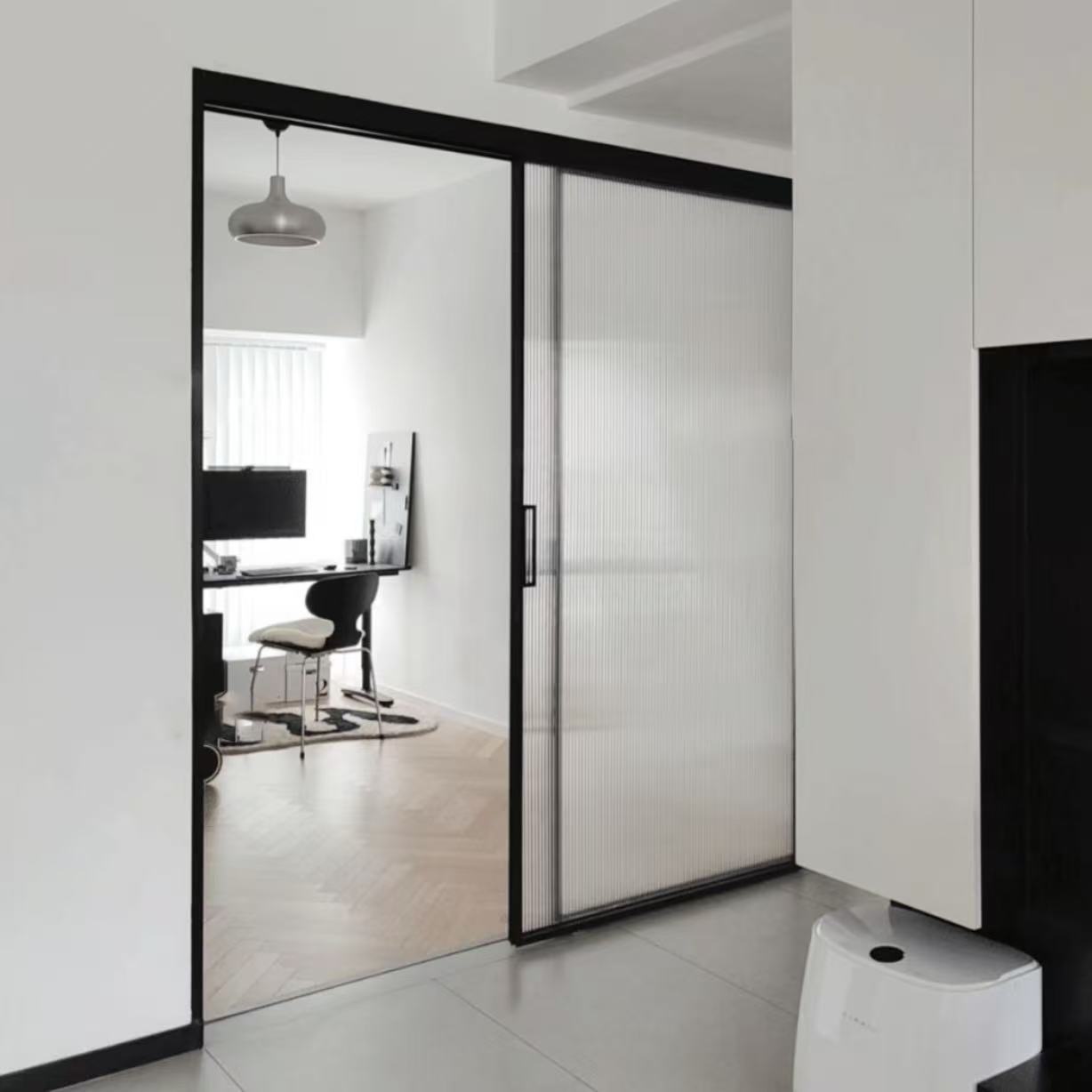
1. Single-Slide Doors
-
One panel slides to the side, ideal for narrow openings.
2. Bi-Parting (Double-Slide) Doors
-
Two panels slide in opposite directions, maximizing entry width.
3. Telescopic Doors
-
Multiple panels slide in a stacked or overlapping manner, suitable for high-traffic areas.
Installation & Maintenance Considerations
Installation Factors
-
Structural Support: Requires a sturdy frame and proper alignment. -
Power Supply: Needs a reliable electrical connection (some models offer battery backups). -
Sensor Placement: Must be calibrated for optimal detection.
Maintenance Best Practices
-
Regular Cleaning: Glass panels should be cleaned with non-abrasive solutions. -
Sensor Calibration: Ensures accurate detection. -
Lubrication: Moving parts require periodic lubrication to prevent wear. -
Professional Inspections: Annual checks help identify potential failures.
Future Trends in Automatic Door Technology
1. Smart Integration
-
IoT Connectivity: Doors can be integrated with building management systems for real-time monitoring. -
AI-Powered Sensors: Advanced motion detection reduces false triggers.
2. Sustainable Materials
-
Eco-Friendly Glass: Recycled and energy-efficient glass options. -
Energy-Harvesting Motors: Regenerative braking to reduce power consumption.
3. Enhanced Security
-
Biometric Access: Fingerprint or facial recognition for secure entry. -
Anti-Tailgating Systems: Prevent unauthorized access.
Conclusion





 Home
Home Sep 29,2025
Sep 29,2025 
 Automatic Glass Sliding Doors: The Silent Architects of Modern Mobility and Architectural Elegance
Automatic Glass Sliding Doors: The Silent Architects of Modern Mobility and Architectural Elegance 
 May 28,2025
May 28,2025