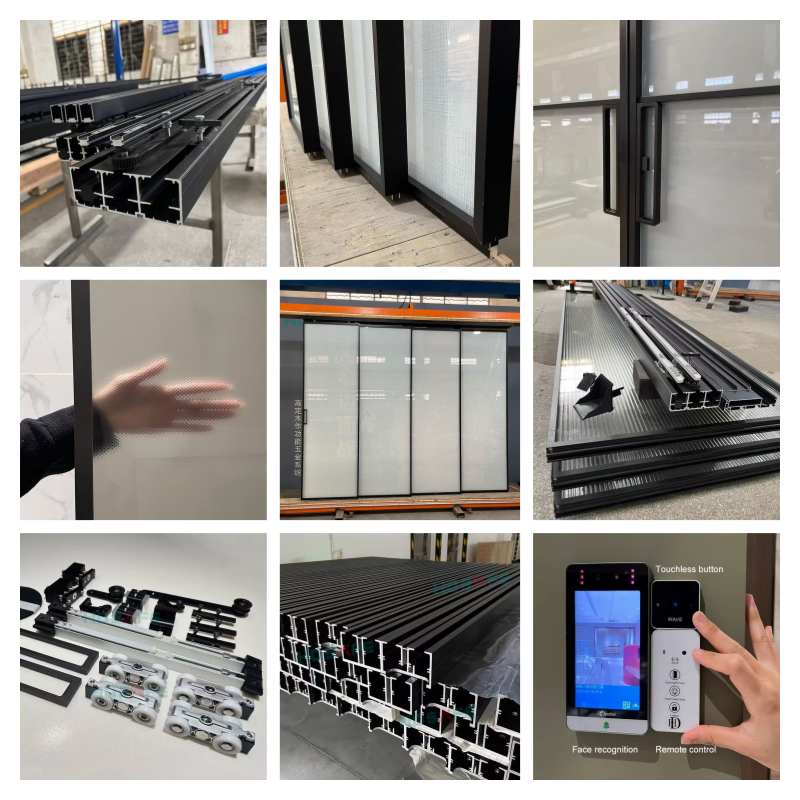
Different Sliding Doors Types for Your Home – A Complete Guide to Styles, Materials, and Benefits (2025)
Meta Description: Explore the ultimate guide to different sliding doors types for your home. Learn about styles, materials, benefits, installation tips, and how to choose the perfect sliding door for your space. Boost your home’s style and functionality today!

Introduction
Sliding doors have become a staple in modern home design, blending aesthetics, functionality, and energy efficiency. Whether you’re renovating your living room, upgrading your patio access, or designing a new home, choosing the right sliding door type can transform your space. In this comprehensive 5000-word guide, we’ll dive deep into different sliding doors types for your home, covering everything from classic designs to cutting-edge innovations.
By the end of this article, you’ll understand:
-
The main categories of sliding doors
-
Pros and cons of each type
-
Materials, finishes, and customization options
-
Energy efficiency and security features
-
Installation considerations and maintenance tips
-
How to match sliding doors with your home’s architecture and lifestyle
Let’s unlock the world of sliding doors and find the perfect fit for your home.
1. Why Sliding Doors Are Perfect for Modern Homes
Before exploring specific types, it’s important to understand why sliding doors are so popular:
1.1 Space-Saving Design
Unlike hinged doors that swing open, sliding doors move horizontally along a track. This eliminates the need for clearance space, making them ideal for small rooms, tight hallways, or areas with limited floor space.
1.2 Seamless Indoor-Outdoor Living
Large glass panels in sliding doors create unobstructed views and easy access to patios, gardens, or balconies, fostering a connection between indoor and outdoor spaces.
1.3 Natural Light Maximization
With expansive glass areas, sliding doors flood rooms with sunlight, reducing reliance on artificial lighting and enhancing mood and productivity.
1.4 Versatility in Design
Available in countless styles, materials, and configurations, sliding doors complement contemporary, traditional, industrial, and minimalist homes alike.
1.5 Increased Property Value
High-quality sliding doors improve curb appeal and functionality, often boosting resale value.
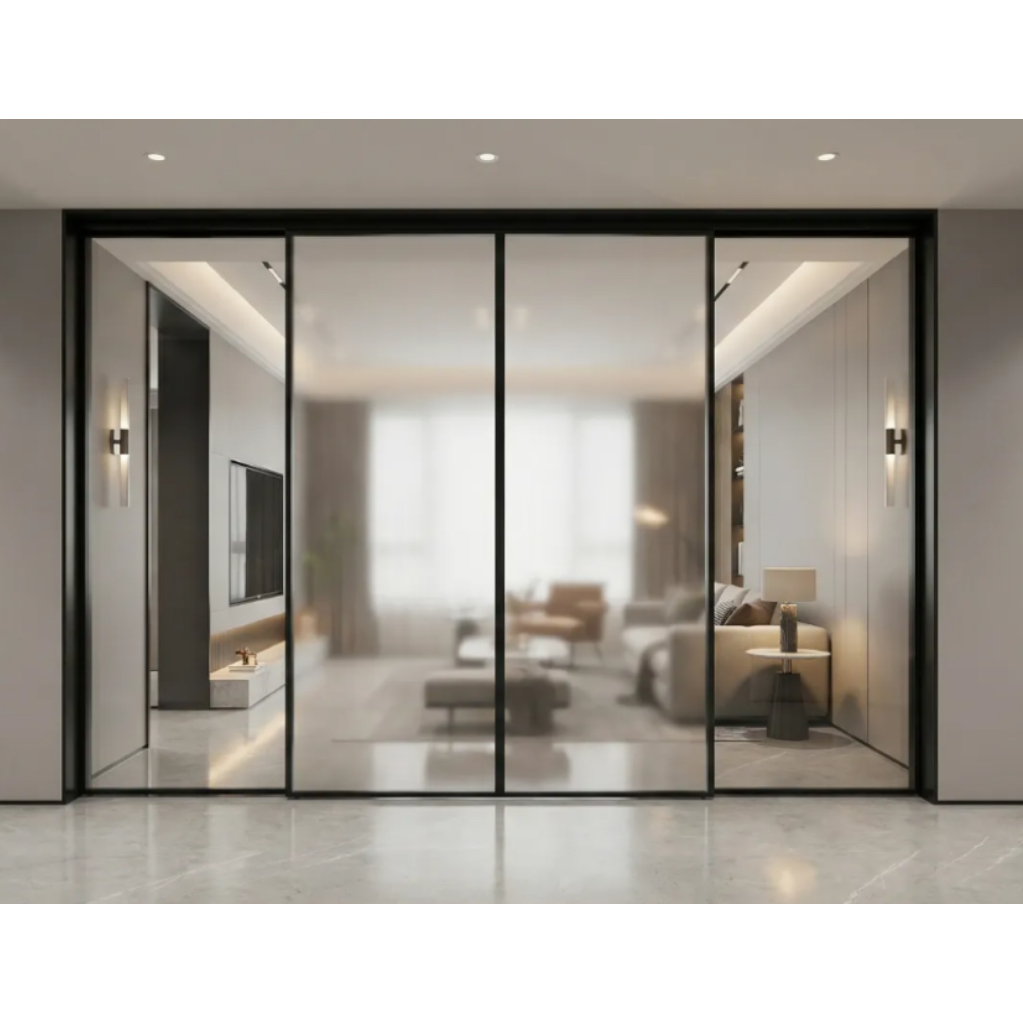
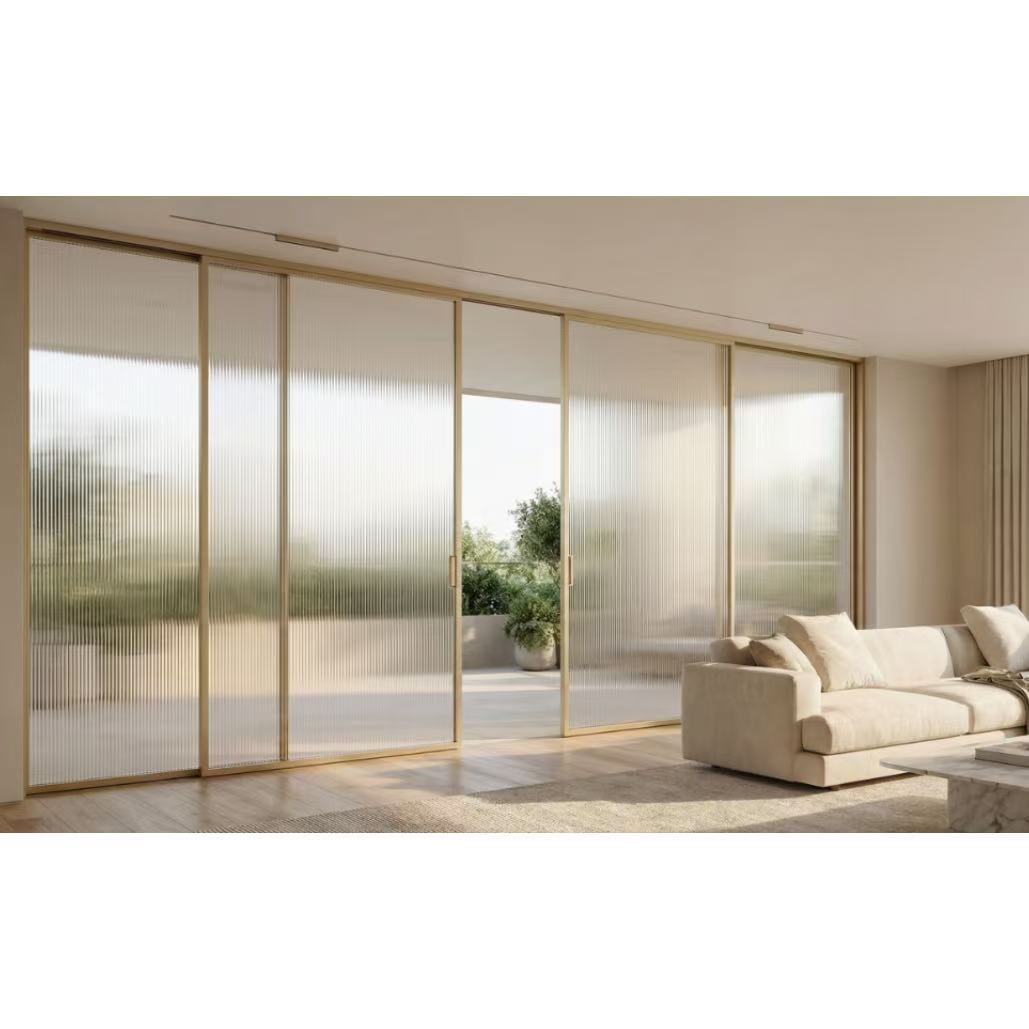
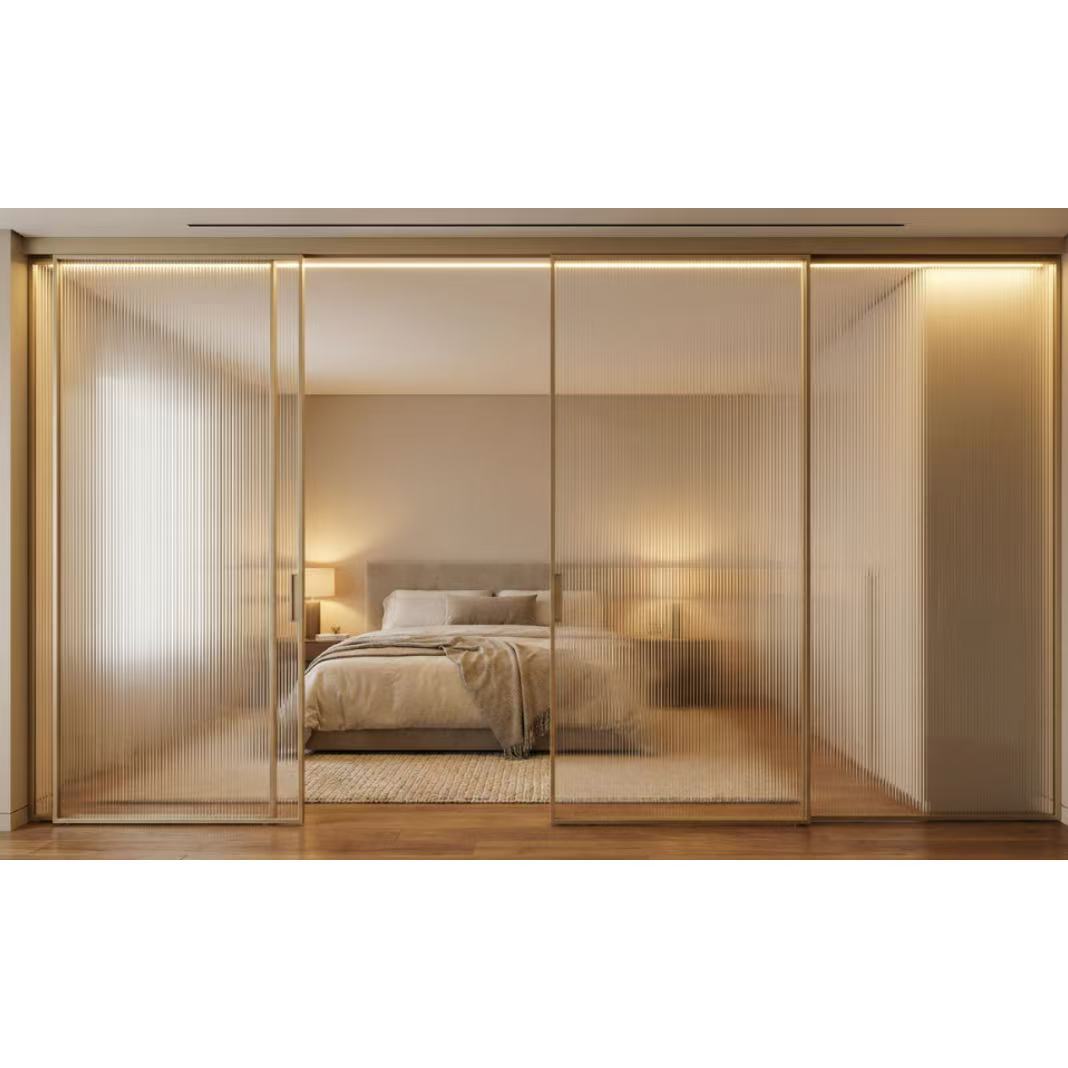
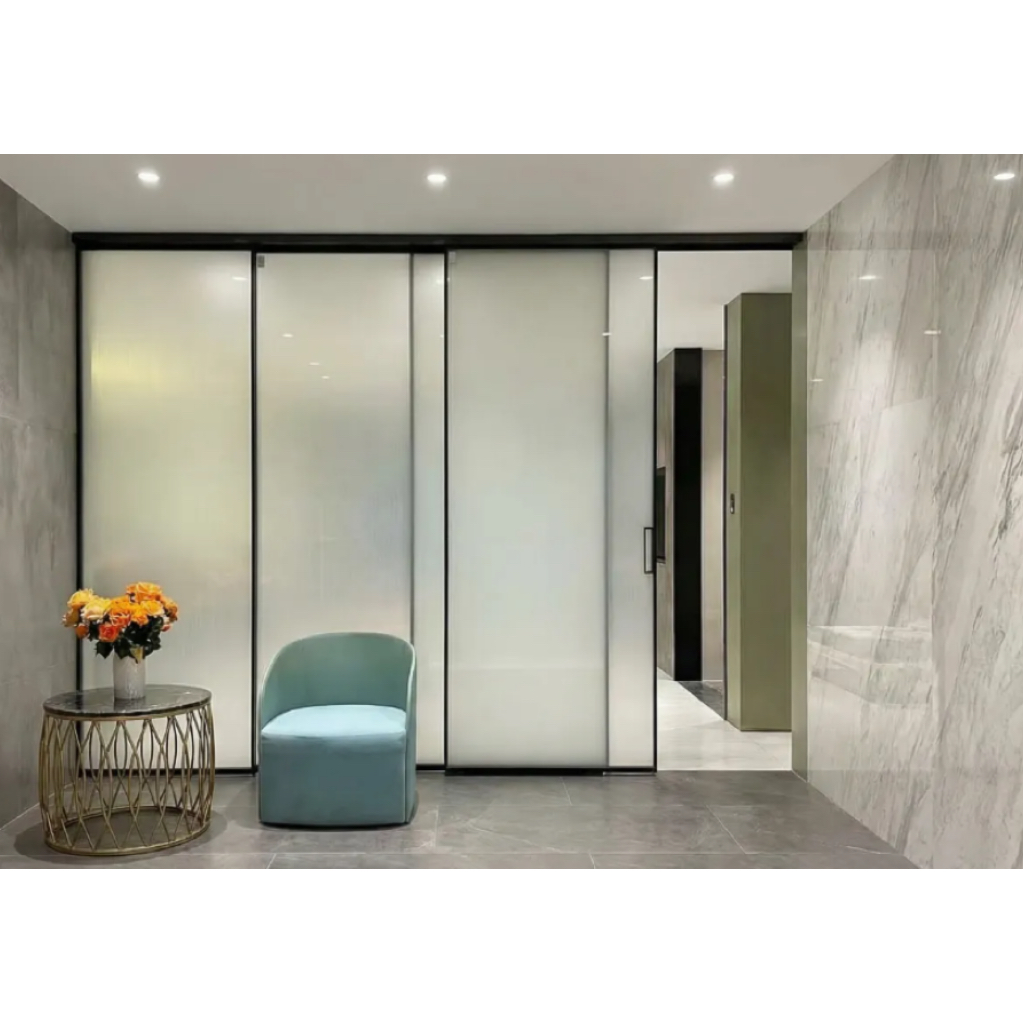




2. Main Categories of Sliding Doors
Sliding doors can be grouped into several broad categories based on operation, structure, and purpose:
-
Standard Sliding Doors
-
Patio Sliding Doors
-
Pocket Sliding Doors
-
Bypass Sliding Doors
-
Folding Sliding Doors (Bi-Fold Doors)
-
Lift-and-Slide Doors
-
Multi-Track Sliding Doors
-
Corner Sliding Doors
-
Security Sliding Doors
-
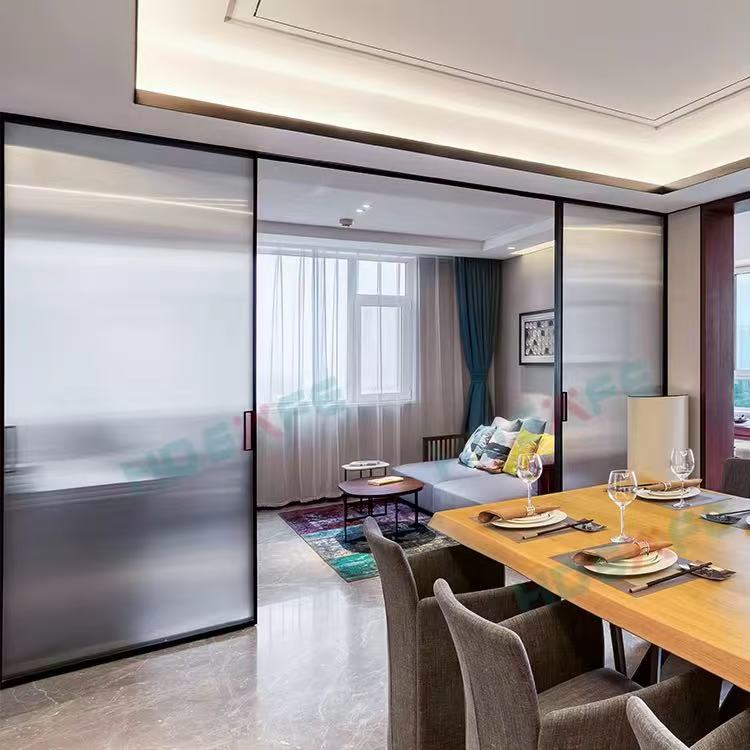
Interior Sliding Doors
We’ll explore each in detail.
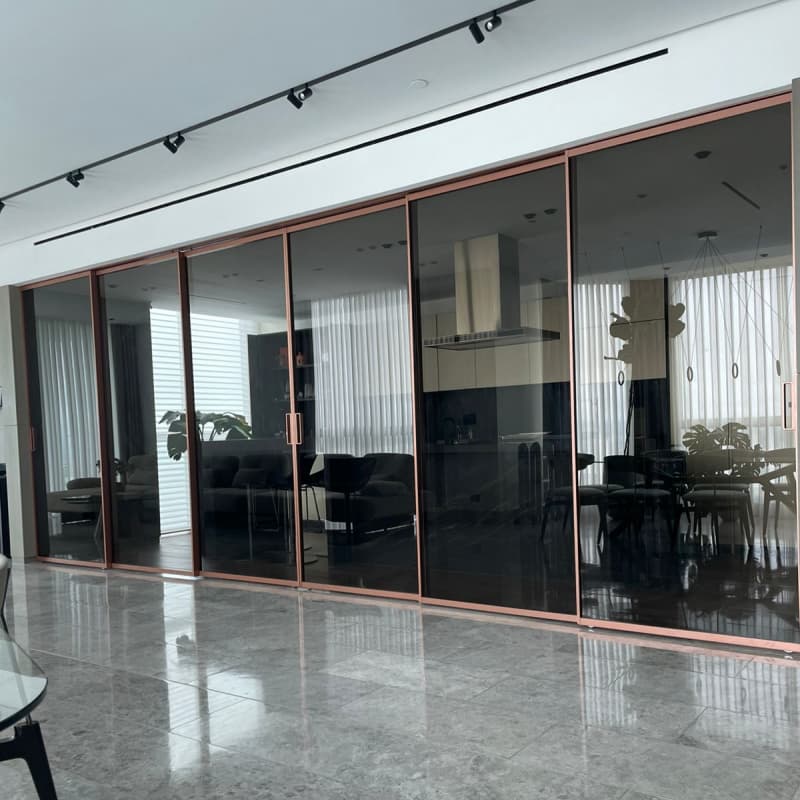
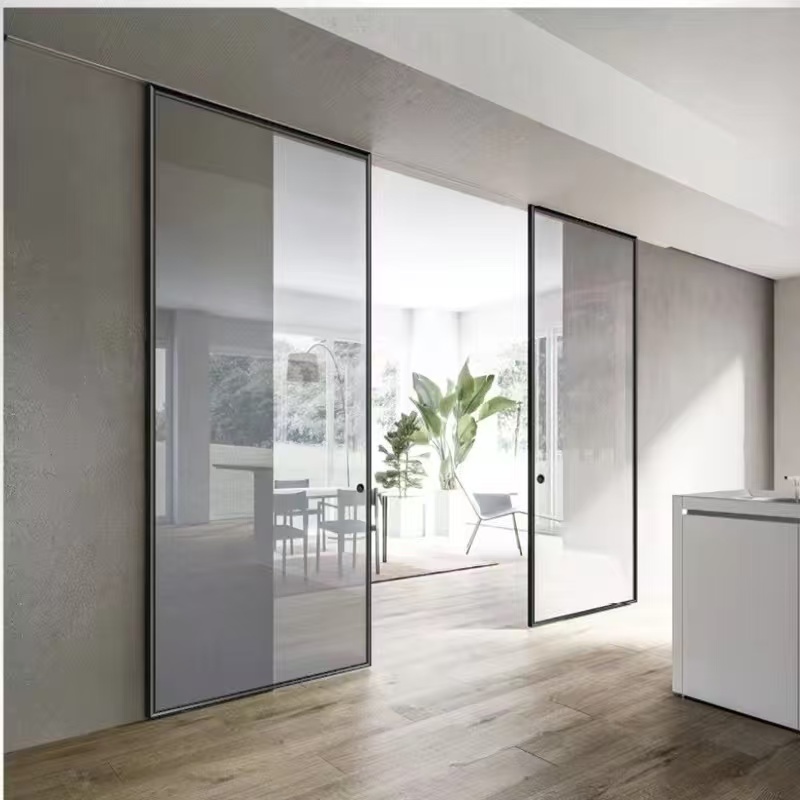
3. Standard Sliding Doors
3.1 Overview
Standard sliding doors consist of two or more panels, where one panel slides past another on a horizontal track. Typically, one panel is fixed, and the other moves, though both can slide in some designs.
3.2 Common Uses
-
Bedroom closets
-
Bathroom entries
-
Room dividers
3.3 Materials
-
Aluminum frames (lightweight, durable)
-
Wood (warm, natural aesthetic)
-
Vinyl (affordable, low maintenance)
-
Composite (wood-aluminum blend for strength and insulation)
3.4 Pros
-
Simple operation
-
Cost-effective
-
Easy to install
3.5 Cons
-
Limited opening width compared to large patio doors
-
May not suit high-traffic areas due to single-track movement
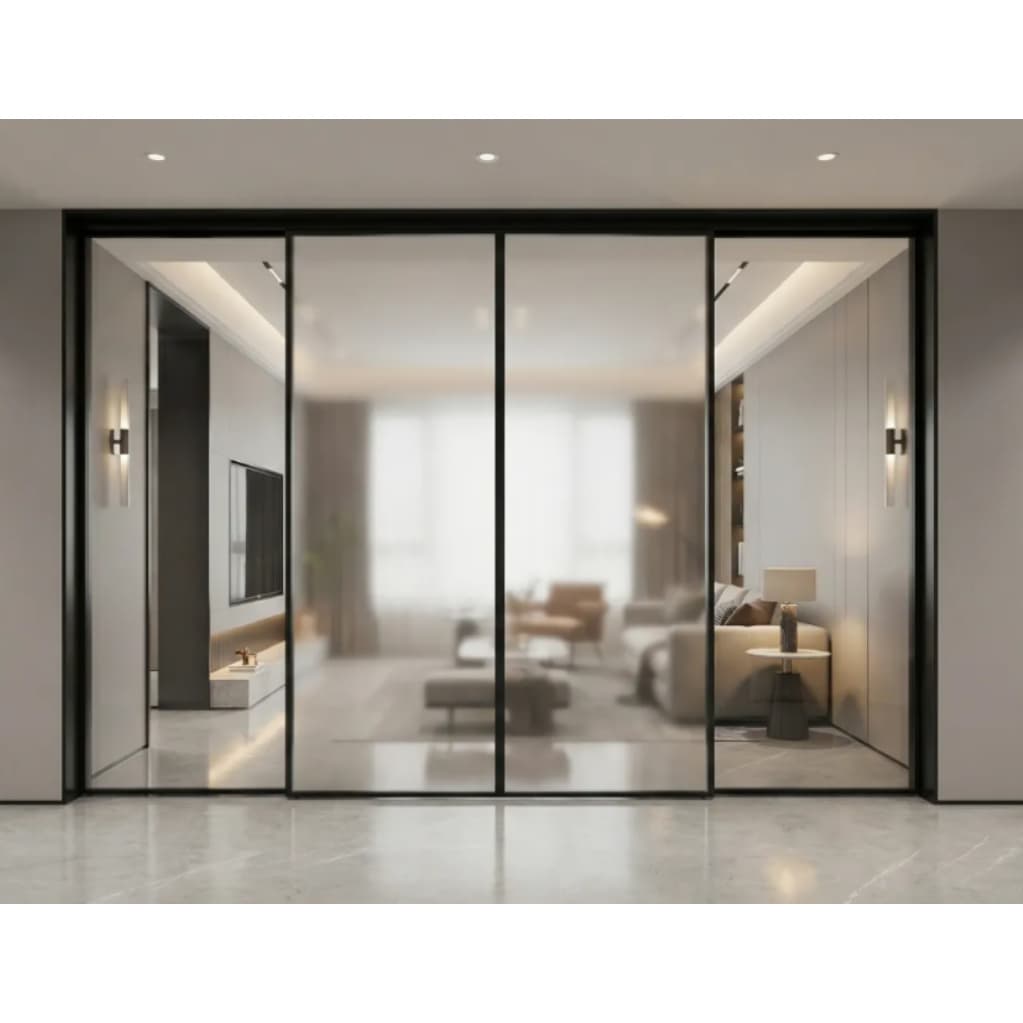
4. Patio Sliding Doors
4.1 Overview
Patio sliding doors are larger versions of standard sliding doors, designed to provide wide access to outdoor spaces. They often feature multiple panels and larger glass surfaces.
4.2 Configurations
-
Two-Panel Sliding Door: One fixed, one operable.
-
Three-Panel Sliding Door: Two panels slide, one fixed, or all three slide depending on design.
4.3 Key Features
-
Tempered or laminated safety glass
-
Weatherstripping for insulation
-
Multi-point locking systems
4.4 Materials & Finishes
-
Powder-coated aluminum (corrosion-resistant)
-
Anodized aluminum (durable, low maintenance)
-
Wood-clad aluminum (combines warmth with durability)
4.5 Pros
-
Expansive views and ventilation
-
Enhances indoor-outdoor flow
-
Available in energy-efficient models
4.6 Cons
-
Higher cost than standard doors
-
Requires sturdy framing for large panels
5. Pocket Sliding Doors
5.1 Overview
Pocket sliding doors slide into a concealed wall cavity, disappearing completely when opened. This creates a seamless, open space without any door obstruction.
5.2 Applications
-
Dividing living and dining areas
-
Hiding home offices or playrooms
-
Creating flexible room layouts
5.3 Construction Requirements
-
Wall must be thick enough to house the door and track system.
-
Structural reinforcement may be needed.
5.4 Materials
-
Solid wood, MDF, or glass panels
-
Metal tracks and rollers for smooth operation
5.5 Pros
-
Maximizes floor space
-
Clean, minimalist look
-
Ideal for open-plan homes
5.6 Cons
-
Complex installation
-
Higher renovation cost if wall modification is required
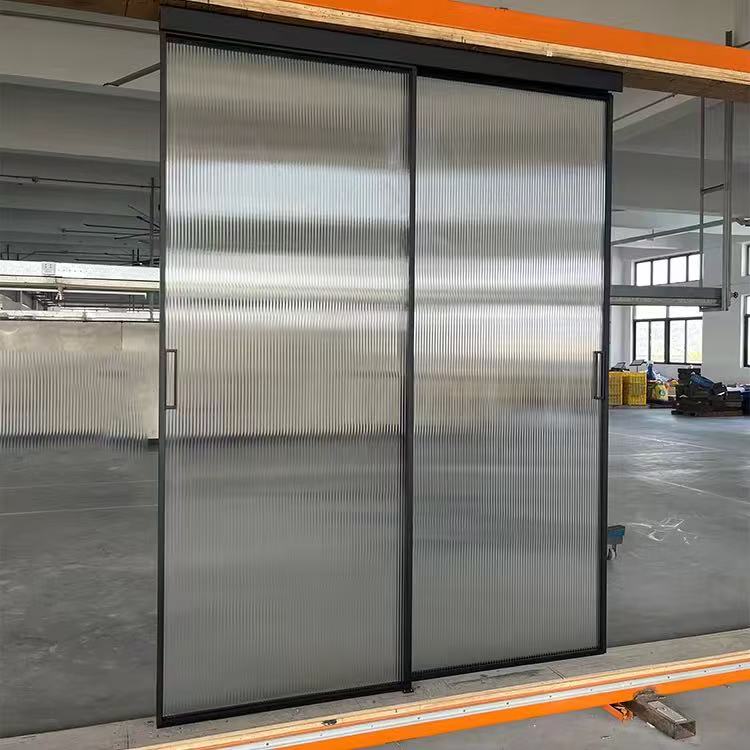
6. Bypass Sliding Doors
6.1 Overview
Bypass doors operate on parallel tracks, allowing two or more panels to slide past each other. Commonly used for closets and partitions.
6.2 Mechanism
Panels overlap slightly as they slide, so the total opening width equals the combined width minus overlap.
6.3 Materials
-
Mirror panels (for closet doors)
-
Frosted or clear glass
-
Wood veneer or painted MDF
6.4 Pros
-
Space-saving alternative to swinging doors
-
Customizable with mirrors or decorative panels
6.5 Cons
-
Overlap reduces full-width access
-
Tracks can collect dust and require cleaning
7. Folding Sliding Doors (Bi-Fold Doors)
7.1 Overview
Though technically not pure sliding doors, bi-fold doors fold back in sections like an accordion, stacking against one or both sides. They offer near-full opening widths.
7.2 Operation
Multiple panels connected by hinges slide and fold to one side.
7.3 Materials
-
Aluminum frames with thermal breaks
-
High-performance glazing
-
Stainless steel hardware for corrosion resistance
7.4 Pros
-
Virtually uninterrupted opening
-
Excellent for large openings and panoramic views
-
Modern, architectural appeal
7.5 Cons
-
More complex mechanism than standard sliders
-
Higher cost and maintenance needs
8. Lift-and-Slide Doors
8.1 Overview
Lift-and-slide doors feature heavy-duty hardware that allows panels to be lifted off the track before sliding. This enables effortless movement of very large, heavy glass panels.
8.2 Key Features
-
Robust multi-point locking systems
-
Seals that engage when panel is closed and lifted
-
Suitable for oversized glass (up to 10 feet wide per panel)
8.3 Materials
-
Thermally broken aluminum for insulation
-
Double or triple glazing for energy efficiency
8.4 Pros
-
Smooth operation even with massive panels
-
Superior weather sealing
-
Luxurious, high-end appearance
8.5 Cons
-
Premium pricing
-
Requires professional installation
9. Multi-Track Sliding Doors
9.1 Overview
Multi-track systems use several parallel tracks to support multiple sliding panels, creating modular walls of glass.
9.2 Configurations
-
Three-track, four-track, or more
-
Panels can slide in either direction independently
9.3 Applications
-
Large commercial spaces
-
Luxury residential patios
-
Partitioning expansive rooms
9.4 Pros
-
Flexible opening arrangements
-
Can cover very wide spans
-
Modern, industrial aesthetic
9.5 Cons
-
Higher complexity and cost
-
Requires precise engineering
10. Corner Sliding Doors
10.1 Overview
Corner sliding doors eliminate the corner post, creating a seamless transition between two perpendicular walls of glass. Often used in contemporary homes with panoramic views.
10.2 Mechanism
Specialized hinges or track systems allow panels to meet at the corner without a vertical mullion.
10.3 Materials
-
Reinforced aluminum or steel frames
-
Laminated safety glass
10.4 Pros
-
Dramatic visual impact
-
Maximizes light and views
-
Unique architectural statement
10.5 Cons
-
High cost and engineering challenges
-
Requires custom manufacturing
11. Security Sliding Doors
11.1 Overview
Designed with enhanced safety features, these doors deter break-ins while maintaining ease of use.
11.2 Security Features
-
Multi-point locking systems
-
Anti-lift devices (prevent panels from being lifted out of tracks)
-
Toughened or laminated glass
-
Reinforced frames
11.3 Materials
-
Steel-reinforced aluminum
-
Impact-resistant glass
11.4 Pros
-
Peace of mind for ground-floor installations
-
Maintains aesthetic appeal
11.5 Cons
-
Heavier and potentially more expensive
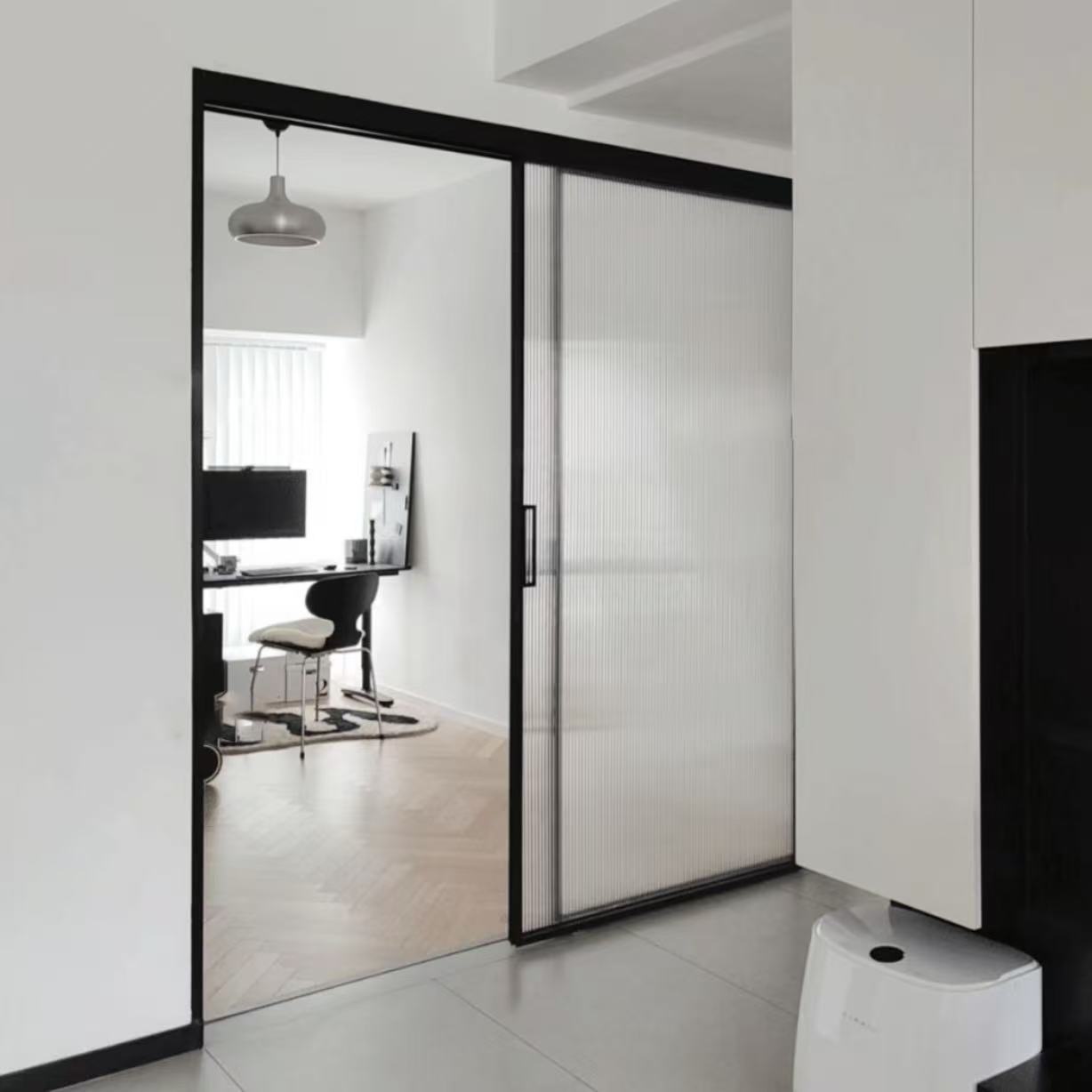
12. Interior Sliding Doors
12.1 Overview
Used inside the home to divide spaces while saving room, interior sliding doors come in various styles and materials.
12.2 Popular Types
-
Barn doors (rustic charm)
-
Glass sliding doors (modern, light-filled)
-
Paneled wooden doors (traditional)
12.3 Materials
-
Reclaimed wood, oak, pine
-
Frosted or textured glass
-
Metal accents
12.4 Pros
-
Adds character and function
-
Ideal for small spaces
12.5 Cons
-
Track systems visible unless recessed
13. Materials Breakdown for Sliding Doors
Choosing the right material affects durability, insulation, and style:
|
Material |
Pros |
Cons |
Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Aluminum |
Strong, slim profiles, low maintenance |
Conducts heat/cold (unless thermally broken) |
Modern, large openings |
|
Wood |
Warm, natural beauty |
Requires maintenance, can warp |
Traditional, interior |
|
Vinyl |
Affordable, good insulation |
Limited color options, less strong |
Budget-friendly homes |
|
Composite |
Combines wood aesthetics with durability |
Higher cost |
Energy-efficient, stylish |
|
Fiberglass |
Strong, low maintenance, good insulation |
Expensive |
Coastal, extreme climates |
14. Glazing Options and Energy Efficiency
Glazing significantly impacts insulation, UV protection, and soundproofing:
-
Single Glazing: Basic, least efficient, rarely used today.
-
Double Glazing: Two panes with gas fill (argon/krypton) for better insulation.
-
Triple Glazing: Three panes, highest insulation, ideal for cold climates.
-
Low-E Coating: Reflects heat, improves energy efficiency.
-
Laminated Glass: Safety glass with interlayer, reduces noise and blocks UV.
-
Tempered Glass: Heat-treated for safety, shatters into small pieces.
Energy Star-rated sliding doors can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 30%.
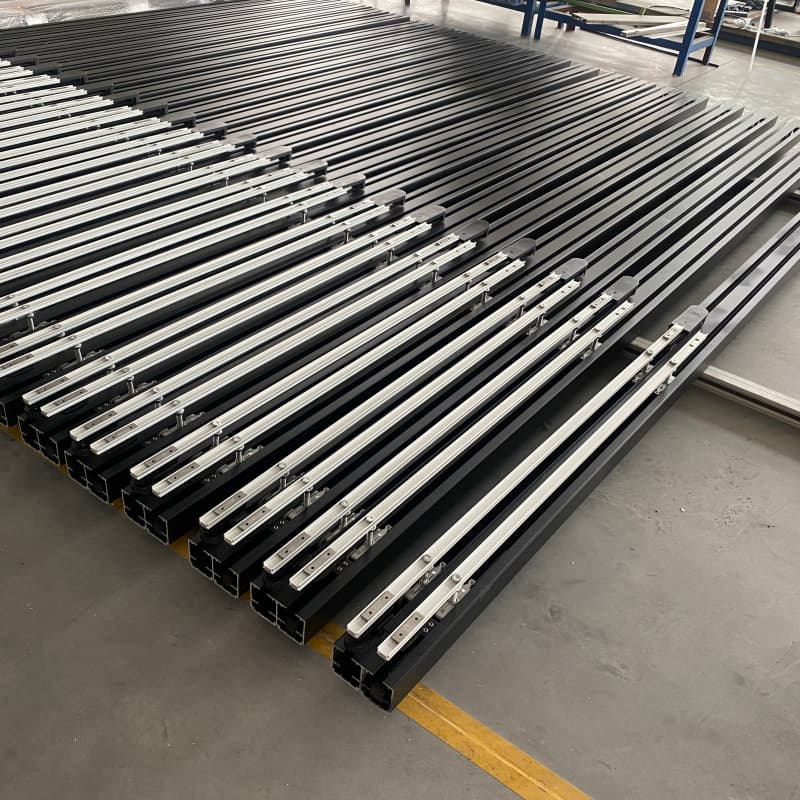
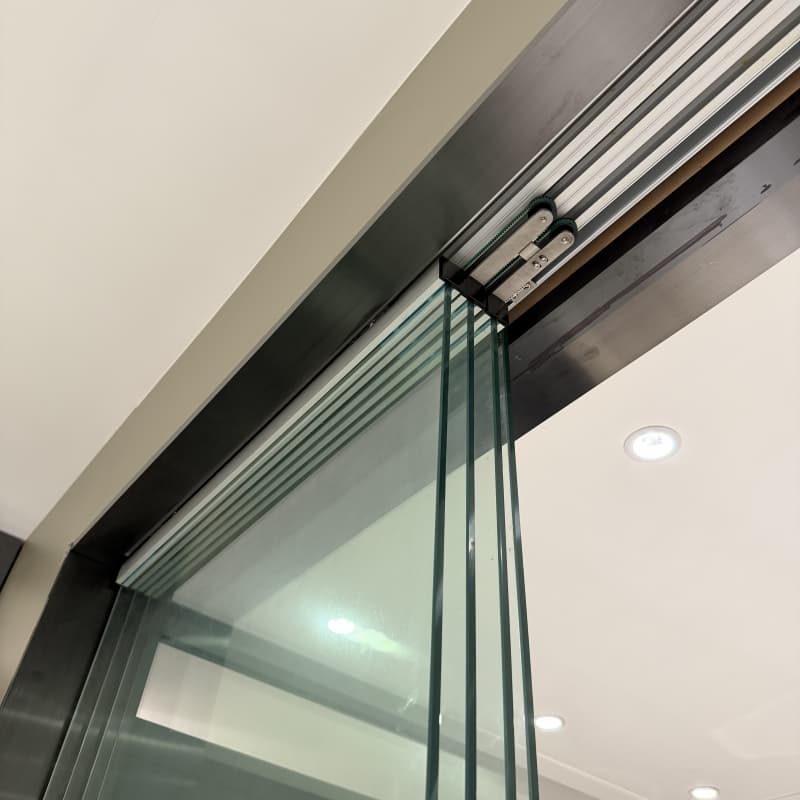
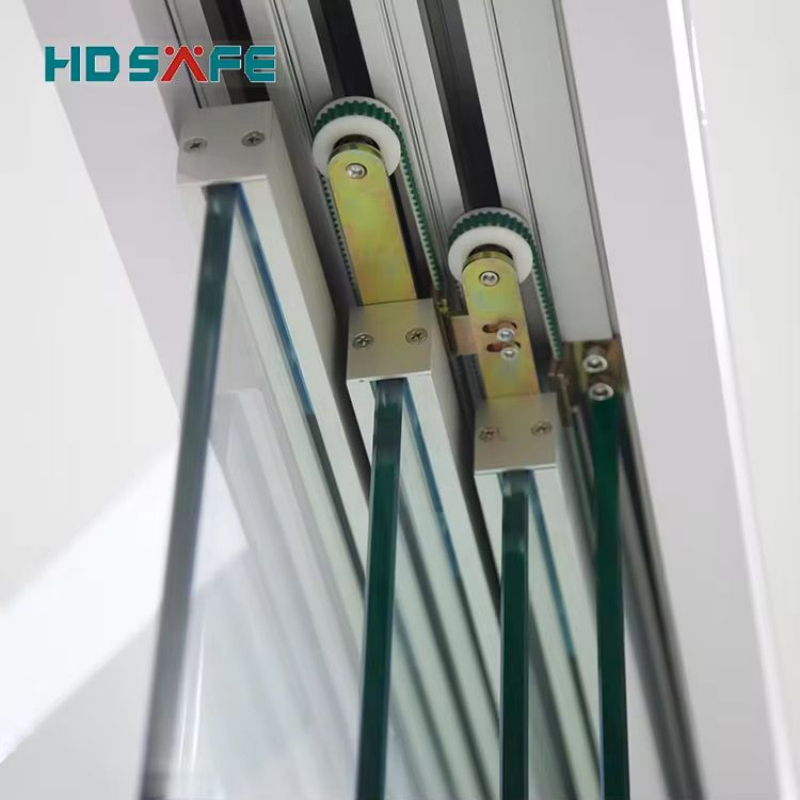
15. Hardware and Accessories
Quality hardware ensures smooth operation and longevity:
-
Rollers: Nylon or stainless steel for quiet, durable movement.
-
Tracks: Aluminum or stainless steel, rust-resistant.
-
Handles and Locks: Ergonomic designs, multi-point locking for security.
-
Seals and Gaskets: Prevent drafts and water ingress.
-
Screens: Retractable or sliding mesh for insect control.
16. Installation Considerations
Proper installation is critical for performance:
-
Level Tracks: Uneven tracks cause sticking or uneven sliding.
-
Wall Structure: Pocket doors need adequate wall depth.
-
Weatherproofing: Proper flashing and seals prevent leaks.
-
Professional vs. DIY: Large patio or lift-and-slide doors should be installed by certified professionals.
17. Maintenance Tips
Extend the life of your sliding doors with regular care:
-
Clean tracks monthly to remove debris.
-
Lubricate rollers and locks annually.
-
Inspect seals and replace if cracked.
-
Check glass for cracks or seal failure.
-
Repaint or refinish wood frames as needed.
18. How to Choose the Right Sliding Door Type
Consider these factors:
-
Space Availability: Pocket doors need wall depth; bypass doors save floor space.
-
Opening Size: Large openings may require lift-and-slide or multi-track systems.
-
Climate: Cold regions benefit from triple glazing and thermal breaks.
-
Security Needs: Ground floors may need reinforced locking.
-
Style Preference: Match frame finish and glass type to home architecture.
-
Budget: Standard sliding doors are affordable; lift-and-slide and corner doors are premium.
19. Trends in Sliding Door Design (2024)
-
Black Steel and Dark Frames: Bold contrast with light interiors.
-
Ultra-Slim Profiles: Maximize glass area for unobstructed views.
-
Smart Integration: Motorized sliding doors with app control.
-
Sustainable Materials: Recycled aluminum and FSC-certified wood.
-
Mixed Materials: Combining wood and metal for texture.
20. Conclusion
Sliding doors are more than functional elements—they’re design statements that enhance light, space, and lifestyle. From classic patio sliders to futuristic lift-and-slide systems, the different sliding doors types for your home offer solutions for every need and aesthetic. By understanding their features, materials, and installation requirements, you can select the perfect sliding door to elevate your home’s comfort, beauty, and value.
Whether you’re aiming for a cozy interior partition or a dramatic indoor-outdoor connection, there’s a sliding door type that fits your vision. Invest wisely, and let your home glide into a new era of style and functionality.





 Home
Home Dec 31,2025
Dec 31,2025 
 The 10 Key Types of Interior Sliding Doors – A Complete Guide to Styles, Materials & Benefits for Your Home (2025)
The 10 Key Types of Interior Sliding Doors – A Complete Guide to Styles, Materials & Benefits for Your Home (2025) 
 Oct 10,2025
Oct 10,2025